Biological Psychiatry Published: May 09, 2021DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.04.024
Fluoroethylnormemantine, a Novel NMDA Receptor Antagonist, for the Prevention and Treatment of Stress-Induced Maladaptive Behavior. Briana K.Chen, Victor M.Luna, Margaret E.Shannon, Holly C.Hunsberger, AlessiaMastrodonato, MichelleStackmann, Josephine C.McGowan, GillesRubinstenn, Christine A.Denny.
Background
Major depressive disorder is a common, recurrent illness. Recent studies have implicated the NMDA receptor in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder. (R,S)-ketamine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, is an effective antidepressant but has numerous side effects. Here, we characterized a novel NMDA receptor antagonist, fluoroethylnormemantine (FENM), to determine its effectiveness as a prophylactic and/or antidepressant against stress-induced maladaptive behavior.
Methods
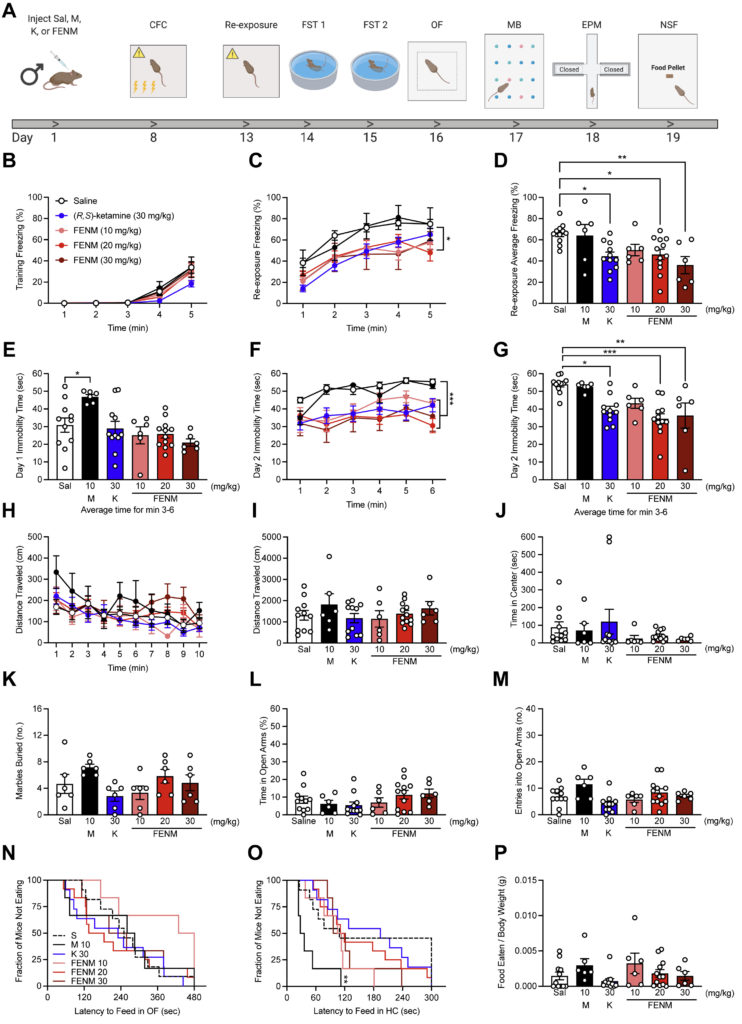
Saline, memantine (10 mg/kg), (R,S)-ketamine (30 mg/kg), or FENM (10, 20, or 30 mg/kg) was administered before or after contextual fear conditioning in 129S6/SvEv mice. Drug efficacy was assayed using various behavioral tests. Protein expression in the hippocampus was quantified with immunohistochemistry or Western blotting. In vitro radioligand binding was used to assay drug binding affinity. Patch clamp electrophysiology was used to determine the effect of drug administration on glutamatergic activity in ventral hippocampal cornu ammonis 3 (vCA3) 1 week after injection.
Results
Given after stress, FENM decreased behavioral despair and reduced perseverative behavior. When administered after re-exposure, FENM facilitated extinction learning. As a prophylactic, FENM attenuated learned fear and decreased stress-induced behavioral despair. FENM was behaviorally effective in both male and female mice. (R,S)-ketamine, but not FENM, increased expression of c-fos in vCA3. Both (R,S)-ketamine and FENM attenuated large-amplitude AMPA receptor–mediated bursts in vCA3, indicating a common neurobiological mechanism for further study.
Conclusions
Our results indicate that FENM is a novel drug that is efficacious when administered at various times before or after stress. Future work will further characterize FENM’s mechanism of action with the goal of clinical development.
Read full paper
Preview of the work :